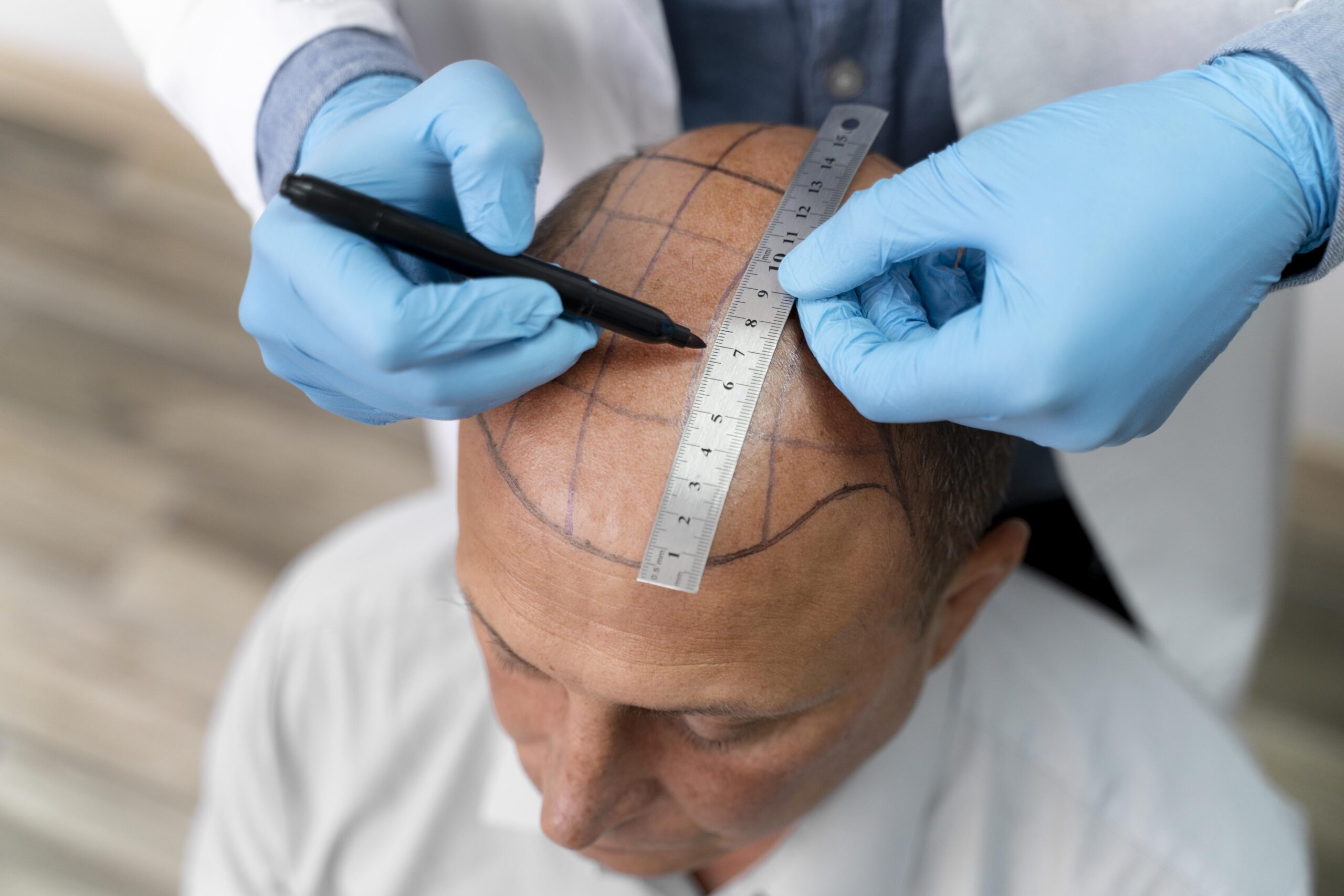
hair transplantation treatment in Bangalore
Hair transplantation is a surgical procedure that involves moving hair follicles from one part of the body (donor site) to a bald or thinning area (recipient site). The primary goal is to restore natural hair growth and improve the appearance of the scalp or other areas affected by hair loss.
Types of Hair Transplantation
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT):
- Description: A strip of skin with hair follicles is removed from the donor area, usually the back of the head. The strip is then dissected into individual follicular units and transplanted into the recipient area.
- Pros: Allows for the transplantation of a large number of grafts in a single session.
- Cons: Involves a linear scar at the donor site, which may be visible if hair is cut short.
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE):
- Description: Individual hair follicles are extracted directly from the donor area using a specialized punch tool and transplanted into the recipient area.
- Pros: Minimally invasive, with no linear scar and quicker recovery time.
- Cons: May require multiple sessions to achieve the desired density and can be more time-consuming.
How Does Hair Transplantation Work?
Consultation and Planning:
- Evaluation: The surgeon assesses the patient’s hair loss pattern, donor area quality, and overall health.
- Design: A treatment plan is created, including the design of the hairline and the number of grafts needed.
Preparation:
- Anesthesia: Local anesthesia is administered to numb the donor and recipient areas.
- Donor Site Preparation: In FUT, a strip of skin is removed. In FUE, individual follicles are extracted.
Transplantation:
- Graft Placement: Hair follicles are carefully implanted into tiny incisions made in the recipient area, following the natural growth pattern of hair.
Post-Procedure Care:
- Healing: The transplanted area may be swollen and tender for a few days. Scabs will form and eventually fall off as the area heals.
- Growth: New hair growth typically begins within 3 to 4 months, with full results visible in 6 to 12 months.
Indications for Hair Transplantation
Androgenetic Alopecia:
- Indication: Commonly known as male or female pattern baldness, where hair loss follows a predictable pattern.
- Suitable For: Individuals experiencing significant thinning or balding, particularly those with sufficient donor hair.
Alopecia Areata:
- Indication: An autoimmune condition that causes sudden, patchy hair loss.
- Suitable For: Patients with stable alopecia areata who have not responded to other treatments.
Traction Alopecia:
- Indication: Hair loss caused by prolonged tension or pulling on hair.
- Suitable For: Individuals who have stopped the source of tension and have residual healthy hair in the donor area.
Post-Surgical or Post-Traumatic Hair Loss:
- Indication: Hair loss resulting from surgical scars or trauma.
- Suitable For: Patients seeking restoration of hair in scarred areas or injury sites.
Cosmetic Hair Restoration:
- Indication: Patients seeking to improve hair density or aesthetic appearance.
- Suitable For: Individuals desiring enhanced hair fullness or reshaping of the hairline.
Contraindications for Hair Transplantation
Uncontrolled Medical Conditions:
- Contraindication: Patients with uncontrolled diabetes, severe hypertension, or other systemic conditions may not be suitable candidates.
- Action: Ensure medical conditions are well-managed before considering hair transplantation.
Inadequate Donor Hair:
- Contraindication: Insufficient donor hair quality or quantity may limit the effectiveness of the procedure.
- Action: Assess the donor area thoroughly to determine suitability.
Active Scalp Conditions:
- Contraindication: Conditions such as active scalp infections or inflammatory diseases can interfere with healing.
- Action: Treat and resolve any active scalp issues prior to the procedure.
Smoking and Alcohol Use:
- Contraindication: Smoking and excessive alcohol use can impair healing and affect results.
- Action: Cease smoking and limit alcohol consumption before and after the procedure.
Realistic Expectations:
- Contraindication: Patients with unrealistic expectations about the outcomes of the procedure may be dissatisfied.
- Action: Ensure a thorough discussion about expected results and limitations.
Post-Procedure Care
Follow-Up Visits:
- Care: Attend follow-up appointments to monitor healing and progress.
- Assessment: The surgeon will assess hair growth and address any concerns.
Scalp Care:
- Instructions: Follow post-procedure instructions for scalp care, including gentle washing and avoiding direct sunlight.
- Medications: Use prescribed medications as directed to manage pain and reduce the risk of infection.
Hair Growth:
- Patience: Understand that new hair growth takes time, and initial results may be gradual.
- Support: Maintain communication with the healthcare provider for ongoing support and adjustments if needed.