mole removal treatment in Bangalore
Definition:
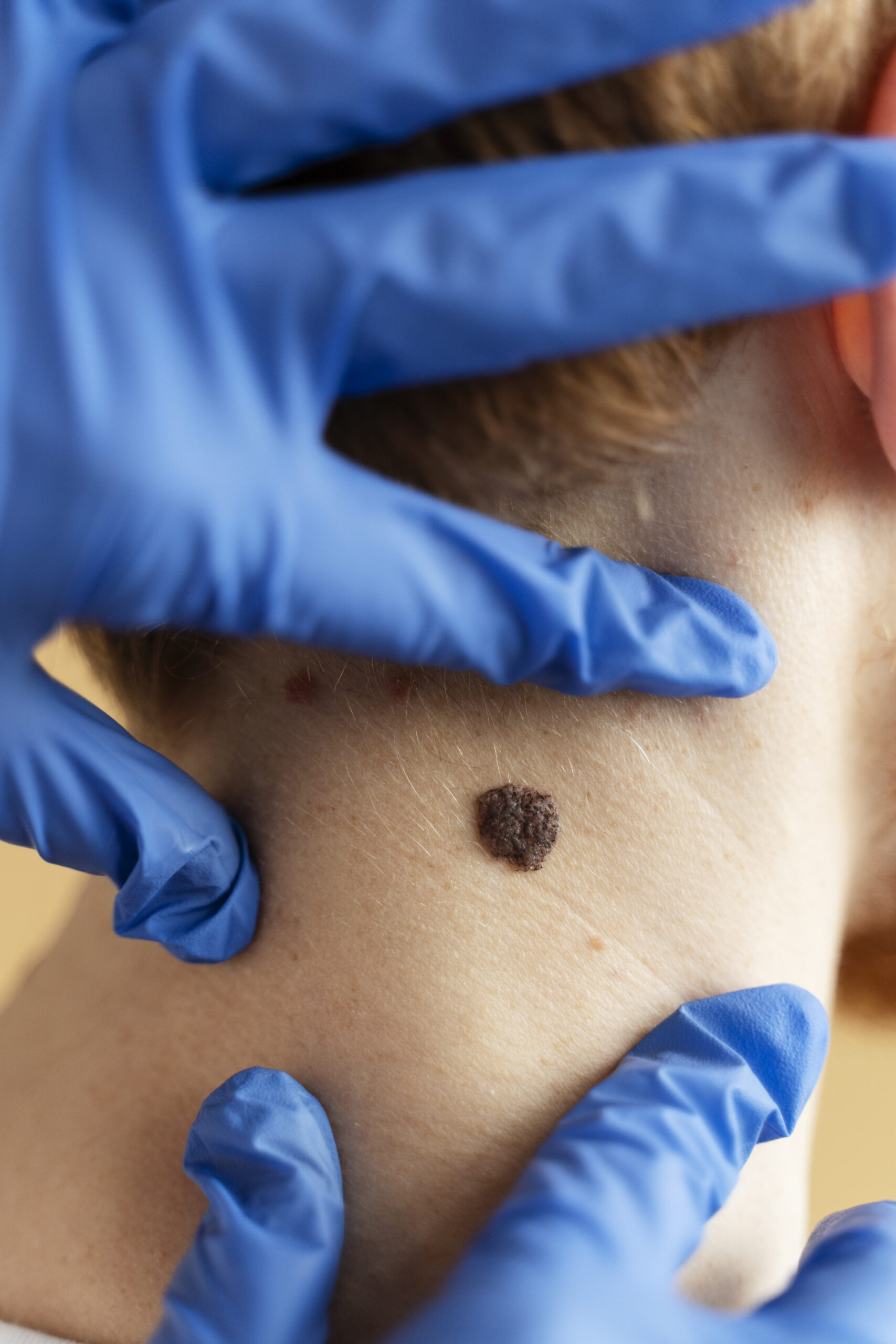
Mole removal is a cosmetic or medical procedure designed to eliminate moles (nevi) from the skin. Moles are common and can appear anywhere on the body. While many moles are benign, removal may be necessary for cosmetic reasons, medical concerns, or discomfort. The procedure can be performed using various methods, each with specific indications and benefits.
Common Methods for Mole Removal
Surgical Excision:
- Description: Involves cutting out the mole along with a margin of surrounding skin.
- Procedure: The area is numbed with a local anesthetic. A scalpel is used to cut out the mole, and the wound is closed with sutures. The removed tissue is often sent to a laboratory for analysis.
- Benefits: Provides definitive removal and is often used for moles that need to be tested for cancer or are deep in the skin.
Shave Removal:
- Description: Involves removing the mole with a small, circular blade that shaves off the mole's surface level.
- Procedure: The mole is shaved off just above the skin level using a sterile blade, usually with local anesthesia. The area is treated with a topical antiseptic.
- Benefits: Minimal scarring and suitable for superficial moles that are not suspected to be cancerous.
Laser Removal:
- Description: Uses focused light beams to destroy the pigmented cells in the mole.
- Procedure: A laser is applied to the mole, breaking down the pigment. Multiple sessions may be required for complete removal.
- Benefits: Non-invasive with minimal downtime. Best for superficial moles and those requiring cosmetic treatment.
Cryotherapy (Freezing):
- Description: Involves applying liquid nitrogen to freeze the mole, causing it to fall off.
- Procedure: Liquid nitrogen is sprayed or applied with a cotton swab to the mole. The mole is frozen, and it typically falls off within a week.
- Benefits: Quick and effective for superficial moles. Minimal discomfort and scarring.
Electrosurgery (Cauterization):
- Description: Uses an electric current to burn off the mole.
- Procedure: An electric current is applied to the mole to vaporize the tissue. Local anesthesia is used to numb the area.
- Benefits: Effective for removing moles with minimal bleeding. Often used for moles that are raised or have irregular borders.
Indications for Mole Removal
Cosmetic Concerns:
- Indication: Moles that are aesthetically unpleasing or located in visible areas where they affect appearance may be removed for cosmetic reasons.
- Suitable For: Patients seeking a more uniform skin appearance.
Medical Concerns:
- Indication: Moles that exhibit changes in size, shape, color, or texture may be removed to rule out or diagnose skin cancer or other skin conditions.
- Suitable For: Patients with moles that show signs of malignancy or atypical changes.
Discomfort or Irritation:
- Indication: Moles that cause physical discomfort or irritation, especially in areas prone to friction (e.g., underarms, collarbones), may be removed to alleviate symptoms.
- Suitable For: Individuals experiencing irritation or discomfort due to the mole.
Preventive Measures:
- Indication: Removal of moles that have a high risk of becoming cancerous based on their appearance or patient’s family history.
- Suitable For: Patients with a history of skin cancer or a high risk of developing it.
Contraindications for Mole Removal
Active Skin Infections:
- Contraindication: Presence of an active skin infection in or around the mole can increase the risk of complications.
- Action: Ensure the infection is treated and resolved before undergoing mole removal.
Certain Medical Conditions:
- Contraindication: Conditions that affect skin healing or increase bleeding risk, such as uncontrolled diabetes or bleeding disorders, may complicate the procedure.
- Action: Discuss any medical conditions with the healthcare provider and manage them appropriately before the procedure.
Pregnancy:
- Contraindication: Some removal methods, particularly those involving lasers or chemicals, may not be recommended during pregnancy.
- Action: Consult with a healthcare provider to determine the safest option if pregnant.
Allergies to Anesthetics or Chemicals:
- Contraindication: Allergic reactions to local anesthetics or chemicals used in certain removal methods may pose risks.
- Action: Inform the practitioner of any known allergies and consider alternative methods if necessary.
Inappropriate Diagnosis:
- Contraindication: Moles should be properly diagnosed to confirm they are benign. Suspicious growths or changes in appearance should be evaluated by a healthcare provider.
- Action: Ensure a proper diagnosis before treatment to rule out potential malignancy.
Post-Procedure Care
Immediate Care:
- Cleaning: Gently cleanse the treated area with mild soap and water. Avoid scrubbing or irritating the area.
- Avoid Picking: Do not pick at or scratch the treated area to prevent infection and ensure proper healing.
Healing:
- Moisturizing: Apply any recommended ointments or creams to keep the area moisturized and support the healing process.
- Sun Protection: Protect the treated area from direct sun exposure using sunscreen or a hat to prevent discoloration or scarring.
Follow-Up:
- Assessment: Schedule a follow-up appointment if needed to monitor healing and ensure that the mole has been fully removed.
- Additional Treatment: If necessary, additional treatments may be scheduled for remaining moles or to address any complications.
Benefits of Mole Removal
Enhanced Appearance:
- Improves skin aesthetics by removing unwanted or unsightly moles, leading to a smoother and more uniform skin surface.
Medical Safety:
- Provides a definitive diagnosis and removal of potentially cancerous moles, reducing the risk of skin cancer.
Relief from Discomfort:
- Alleviates physical discomfort or irritation caused by moles, especially in areas prone to friction.